The Pregnancy timeline

Pregnancy has a beginning and an end. To step into the vehicle of pregnancy and start on the road ahead is for most scary, especially if you haven't been on this road before!On this road many stops is designed, mostly by experience gained by other travelers who went down this road before.This will be an attempt to outline the road ahead, and especially map the stops, and why one need to stop at these points on the road: most of these stops are markers down the road where expected changes happened.
They represent moments in time where one can, with certainty, look through a window at the pregnancy and its product, the baby, to enable us to make the all important diagnosis of normality, or the deviations from normality.Obviously will the process of mapping be easier with a travel previously down this road. In these cases our mapping will follow to a certain extent the previous experiences.
This Pregnancy timeline is especially for the first timers: the so called primigravida. Even in them some special circumstances may apply, and in these cases individualization will demand its own stops.To timeframe pregnancy will always be difficult: to begin with the fertilization of the egg is impossible: not everyone remembers the big moment (big bang?) when sperm takes on egg and produces another human being.It is universally agreed that the first day of the last menstrual period must be the date that notify the beginning: thus is our timeline two weeks ahead. A Mean of 40 weeks is the agreed length of pregnancy if these two weeks is applied.
Standing back from this one can divide pregnancy roughly into 3 unequal parts, called trimesters (1st, 2nd, and 3rd trimesters).
The 1st trimester will be up to 12 weeks ( this is the embryonic phase in which the single sperm and single egg unite into one cell, which divide into two parts and then 4 and then 8, and so forth, until at 12 weeks pregnancy all the organs of the future human being is formed).The 2nd and 3rd trimesters are the period during the pregnancy in which the embryo (now called a fetus or fetus) grow and start to ripen. This grow phase last until the end of puberty, and some people keep on developing until old age (some never finish this developmental phase!).
To demarcate the border or transition time in our timeline between the 2nd and 3rd trimester is not universally agreed upon. It has all to do with the viability of the growing fetus. This had traditionally been 28 weeks, but with the increasing acumen of pediatricians to save babies at an earlier stage of the pregnancy, this cutoff went earlier and earlier. It is at different periods pending on the community in which you are, but as early as 20 weeks had already being suggested. For practical purposes one can put it down to be somewhere between 26 and 28 weeks of pregnancy.
Looking at the possible stations on the road down the first trimester one do see a few possible stops. Obviously do one need to have your pregnancy diagnosed: and this happen secondary to a loss- the missing of the all too present menstruation, especially for those wanting ( or screaming) for a pregnancy. The most accurately test is the urine pregnancy test, which is positive as early as the 5th day after the missed period. Ultrasound confirmation is present at 5 weeks amenorrhea, but do not expect too much! At the 7 weeks stop one see much more: a sac (and confirmation of the amount of embryos) plus the all important heartbeat. Measuring the length of the embryo, and thereby estimating the big day when the 40th week will arrive is now possible. All these ultrasound measurements and observations are at this stage easier with a vaginal ultrasound probe. Between the 10th week and the 12th week one can get additional information regarding the embryo in the sense that the nucaltranclucancy can be measured (important in the screening for Down’s syndrome). This is also the time when a biopsy from the placenta (through the abdominal wall) can be done if any genetic assessments of the embryo are advisable.
Important happenings in the first trimester include the arrival of so-called "minor" symptoms of pregnancy, of which nausea and vomiting is the "major" pests. All important support and education of the pregnant lady is the bulk of the role of the caregiver in this period of pregnancy.
Calamities that can happen in this trimester are part of the screening process for normality: genetic abnormalities, especially those that are incompatible with live, leads in this period to spontaneous abortions. The bulk of spontaneous abortions that happen before the 12th week of pregnancy are due to genetic malformations - malformations over which there is no control from a medical point of view. To add to our inability to control this period: these abortions are normally complete and no further treatment (curettage) is usually needed. In the event of vaginal bleeding in this period the normal "treatment” consists thus out of observing the presence of an intra-uterine pregnancy and the presence of the fetal heartbeat, and in the event of bleeding with clots and pain, if any products of pregnancy is still present in the uterus, by means of an ultrasound.
Another calamity is a pregnancy outside the confinements of the uterine cavity: an extra uterine pregnancy, or ectopic pregnancy. This usually follows a specific symptom timeframe: a sudden onset of a sharp stabinglike lowers abdominal pain (due to bleeding in the abdominal cavity) with or without vaginal bleeding that follows. The most common time for this to happen is after 8 weeks amenorrhea.
the developing embryo

The second trimester is basically a quiet time as far as the caregiver is concerned. It's a time of growth of the fetus. There are during this period only two important stops: round about the 16th week is the time when a amniocentesis (withdrawal of amniotic fluid through the abdominal wall under supervision of an ultrasound - the amniotic fluid contains fetal cells that can be grown and genetically assessed) can be done to take something out of the world of the fetus to be tested, if indicated. A much less invasive test is the so-called “triple test”, where the risk for Down’s syndrome is done with a simple blood test. It is basically a screening test whereby the pregnancies at low risk are excluded from those that needed an amniocentesis.
With the ultrasound examination at 20 weeks, where the fetus is assessed for structural normality, placental localization and gestational age is determined, the booking visit is completed: the pregnant women can now been “classified" into than categories of low risk and high risk pregnancies, and referred to the appropriate health worker who will attend to her pregnancy’s further follow-up. Once again is one of the key roles of the health worker to be available when needed and to be able to communicate the necessary problem solving.
developement of the foetus in second trimester
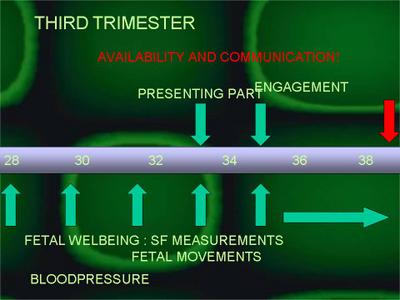
It is in the third trimester where the real guarding of the pregnant woman and her fetus starts. With the fetus now viable, the sometimes “godlike" role of the caregiver takes root.
The biggest question to answer with any calamity in this period is: Is the fetus better off inside or outside the uterus? And if it is decided to terminate the pregnancy: What is the preferred route of delivery?
It is also the period of pregnancy in which the burden of the pregnancy on the woman's body is the highest.Because of this and because of the viability chance of the fetus, the frequency of monitoring of the pregnant woman is increased. At a two weekly (it can be more frequent, or less frequent pending on circumstances) visit until the thirty fourth week, and then weekly till birth, especially the blood pressure is monitored. With this fetal growth is monitored, preferably by serial measurements of the fundal height (the distance from the upper border of the symphisis pubis and the top of the uterus, in the midline). Fetal wellbeing is also monitored by the woman herself by observing the fetal movements.With each visit from the 34th week onwards, the abdomen needs to be palpated to assess what is presenting above the pelvis (the baby turns now with it's head presenting), and after 36 weeks (in the firs timers!) if the head is going down into the pelvis (engagement: it is a predictor of normal birth if it happen, if it doesn’t happen a may be the first sign of disproportion- head too big to go down through the birth canal with delivery).It is especially during this period that the caregiver must be available at all times!
We arrived at our destination when the pregnancy timeline reached 38 weeks, the water broke or the "pains" of uterine contractions starts.
developement of the foetus in the third trimester








1 Comments:
Who knows where to download XRumer 5.0 Palladium?
Help, please. All recommend this program to effectively advertise on the Internet, this is the best program!
Een reactie posten
<< Home